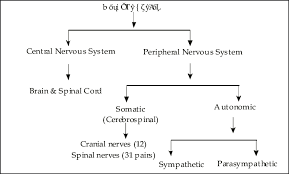
The Central Nervous System (CNS) – The Command Center of the Human Body
The human body is an intricate and complex machine, and at the heart of its functioning lies the Central Nervous System (CNS). The CNS acts as the command center, processing information and controlling various functions necessary for survival. Understanding the CNS is crucial for comprehending how we move, think, feel, and respond to our environment.
What is the Central Nervous System?
The Central Nervous System (CNS) consists of two primary components:
The Brain – The control center that processes information, regulates bodily functions, and enables cognitive abilities.
The Spinal Cord – The communication pathway that transmits signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
The CNS works in coordination with the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) to relay sensory input and motor responses, ensuring smooth body functioning.
Functions of the CNS
The CNS is responsible for several critical functions, including:
1️⃣ Processing and Interpreting Sensory Information
The CNS receives sensory input from the body through sensory neurons.
It processes stimuli such as touch, temperature, pain, and sound.
2️⃣ Regulating Motor Functions
The CNS sends signals to muscles and glands via motor neurons.
It controls voluntary movements (e.g., walking) and involuntary movements (e.g., heartbeat, reflexes).
3️⃣ Cognition and Emotions
The CNS enables thinking, reasoning, memory, and problem-solving.
It regulates emotions such as happiness, fear, and anger.
4️⃣ Maintaining Homeostasis
The CNS controls body temperature, blood pressure, and hormone secretion.
It ensures that the internal environment remains stable despite external changes.
Components of the CNS
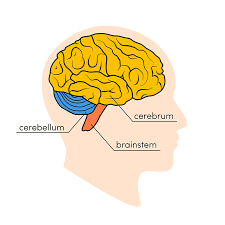
🧠 The Brain: The Control Center
The brain is the most complex organ in the body, consisting of billions of neurons. It is divided into different parts, each performing specific functions:
1. Cerebrum (Largest Part of the Brain)
Responsible for thinking, learning, emotions, and voluntary actions.
Divided into two hemispheres (left and right), each controlling opposite sides of the body.
Contains four lobes:
Frontal Lobe: Decision-making, movement, problem-solving.
Parietal Lobe: Sensory processing, spatial awareness.
Temporal Lobe: Memory, hearing, language.
Occipital Lobe: Visual processing.
2. Cerebellum (The Coordinator)
Controls balance, coordination, and fine motor movements.
Helps in maintaining posture and muscle tone.
3. Brainstem (The Life-Support System)
Connects the brain to the spinal cord.
Regulates breathing, heart rate, digestion, and sleep cycles.
Divided into Midbrain, Pons, and Medulla Oblongata.
🧬 The Spinal Cord: The Information Highway
The spinal cord is a long, tube-like structure that extends from the brainstem down the vertebral column. It serves as:
A communication pathway, transmitting signals between the brain and body.
A center for reflex actions, such as the knee-jerk response.
How the CNS Communicates?
The CNS communicates through neurons, specialized cells that transmit electrical and chemical signals.
Sensory Neurons carry information from the body to the CNS.
Motor Neurons send instructions from the CNS to muscles and glands.
Interneurons connect neurons within the CNS to process information.
Neurons communicate using neurotransmitters such as dopamine, serotonin, and acetylcholine, which play vital roles in mood, memory, and muscle function.
Common Disorders of the CNS
The CNS is vulnerable to various diseases and disorders, including:
🧠 Neurodegenerative Diseases
Alzheimer’s Disease: Causes memory loss and cognitive decline.
Parkinson’s Disease: Affects movement and coordination.
🦠 Infections
Meningitis: Inflammation of the brain and spinal cord membranes.
Encephalitis: Brain inflammation caused by viral infections.
🩸 Trauma and Injuries
Spinal Cord Injury: Can lead to paralysis.
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI): Can cause cognitive impairment.
🔄 Autoimmune Disorders
Multiple Sclerosis (MS): The immune system attacks the protective covering of neurons.
Guillain-Barré Syndrome: Causes nerve damage, leading to weakness and paralysis.
How to Keep Your CNS Healthy?
Maintaining CNS health is crucial for overall well-being. Here are some essential tips:
🍏 1. Eat a Brain-Healthy Diet
Consume Omega-3 fatty acids (found in fish, walnuts) for neuron function.
Eat antioxidant-rich foods (berries, dark chocolate) to protect brain cells.
Stay hydrated and limit processed foods.
🏋️♂️ 2. Exercise Regularly
Physical activity boosts blood flow to the brain and releases endorphins.
Yoga and meditation help reduce stress and improve cognitive function.
😴 3. Get Enough Sleep
Sleep helps in memory consolidation and neuron repair.
Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
🧘 4. Manage Stress Effectively
High stress can damage the nervous system.
Practice mindfulness, deep breathing, and relaxation techniques.
🏥 5. Protect Your Brain and Spinal Cord
Wear helmets and seat belts to prevent head and spinal injuries.
Avoid drugs and excessive alcohol, as they impair CNS function.
📚 6. Keep Your Brain Active
Engage in activities like reading, puzzles, and learning new skills.
Social interaction and hobbies help maintain cognitive function.
Conclusion
The Central Nervous System (CNS) is the control center of our body, managing everything from thoughts to movements. Keeping it healthy is essential for a long, active, and fulfilling life. By following a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, and mental exercises, we can ensure our CNS remains strong and efficient.
Understanding the CNS not only helps us appreciate the complexity of our body but also enables us to take better care of our neurological health. A well-maintained nervous system leads to a better quality of life, improved cognitive abilities, and enhanced overall well-being. 🚀
By-Ubaid ishaq lone
(Member of Alpha foundation)







.png)


Comments
Post a Comment