Commonly Used Instruments in Experimental Pharmacology Laboratory
Experimental pharmacology is an essential field that helps us understand how drugs work in living organisms. Scientists use various instruments to test drug effects on isolated tissues and whole animals. Let’s explore these instruments in detail in simple and easy-to-understand language.
1. Instruments for Whole Animal Studies
These instruments help in studying drug effects on live animals like rats and mice.
A. Behavioral Studies
1. Rotarod Apparatus
This instrument tests the muscle coordination and balance of rodents.
A rod keeps rotating, and the animal has to maintain its grip.
If the animal falls, the time is recorded to assess muscle function.
2. Actophotometer
This is used to measure the movement or locomotor activity of animals.
It works with light beams; when the animal moves, it interrupts the beam, and the activity is recorded.
3. Electroconvulsometer
Used to study seizures and test anticonvulsant drugs.
It delivers an electric shock to the animal and records convulsions to analyze drug effects.
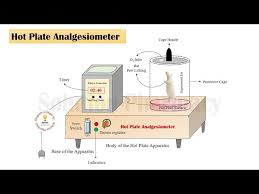
4. Analgesiometer (Eddy’s Hot Plate, Tail Flick Test)
This instrument measures the pain threshold and painkiller effectiveness.
In the hot plate test, the animal is placed on a heated surface, and the time taken to react (licking paws or jumping) is recorded.
In the tail flick test, heat is applied to the tail, and the reaction time is measured.
B. Anti-Inflammatory Studies
5. Plethysmometer
This device measures swelling or edema in an animal’s paw to test anti-inflammatory drugs.
The swollen paw is dipped in the instrument, which calculates the size and records the reduction in inflammation after drug treatment.
C. Cardiovascular Studies
6. Blood Pressure Recorder
This instrument is used to measure blood pressure changes in animals after drug administration.
It works by placing a cuff on the tail of the animal and recording pressure changes.
7. ECG Machine
It records the electrical activity of the heart to monitor how drugs affect heart function.
Electrodes are attached to the animal, and heartbeats are displayed on a screen.
2. Instruments for Isolated Tissue Experiments
These instruments help in studying drug effects on specific organs like the heart, intestine, and trachea outside the body.
A. Tissue Preparation Apparatus
8. Organ Bath
This is used to keep tissues (like intestine, uterus, or trachea) alive while testing drug effects.
The tissue is placed in a solution with oxygen and nutrients to mimic body conditions.
When a drug is added, changes in contraction or relaxation are recorded.
9. Sherrington’s Kymograph
This instrument records muscle or tissue movement after drug administration.
A tissue is attached to a lever that moves and marks changes on a rotating drum.
10. Langendorff Apparatus
This is used to study how drugs affect an isolated heart.
The heart is kept alive using oxygenated liquid, and changes in heartbeat or contraction force are recorded.
B. Aeration & Temperature Control
11. Oxygen Cylinder & Aerator
These provide oxygen to isolated tissues, ensuring their survival during drug testing.
Tissues need a continuous oxygen supply to function properly in lab experiments.
12. Thermostat
It maintains a constant temperature for experiments.
Most tissues work best at 37°C (body temperature), and this device ensures they don’t overheat or cool down.
3. Instruments for Drug Analysis
These instruments help in measuring and analyzing drug properties.
13. UV-Visible Spectrophotometer
This device measures how much light is absorbed by a drug solution.
It helps determine drug concentration and purity.
14. Fluorimeter
Used to analyze drugs that emit light (fluorescence) under UV light.
It is used to detect very small amounts of drugs in solutions.
15. Centrifuge
This device spins samples at high speed to separate liquids from solids.
It is used in blood or tissue sample preparation before analysis.
16. pH Meter
It measures the acidity or alkalinity of drug solutions.
Many drugs require a specific pH for stability and effectiveness.
4. Instruments for Drug Formulation & Testing
These instruments test how drugs are formulated and released.
17. Tablet Dissolution Apparatus
It checks how quickly a tablet dissolves in liquid.
This is important for ensuring drugs release at the right time in the body.
18. Disintegration Test Apparatus
Measures how fast a tablet breaks apart after swallowing.
Tablets must disintegrate quickly so they can be absorbed in the body.
19. Friability Tester
Tests how strong a tablet is by rotating it in a drum and measuring weight loss.
Weak tablets may break easily, making them ineffective.
Conclusion
These instruments are essential in pharmacology labs for testing drug actions on tissues and whole animals. Understanding how they work helps scientists develop safer and more effective medicines.
@alpha_help_foundation




















.png)


Comments
Post a Comment